User Tools
Sidebar
This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Case C 2: Cubic cloud
Setup:
- simple cubic cloud
- domain: 7×7 km$^2$ in x-y-plane, 5 km in z direction
- cubic cloud 1x1x1 km$^3$ in domain center: x: 3-4km, y: 3-4km, z: 2-3km
- 70×70 pixels along x-y direction
- periodic boundary conditions
- vertical optical thickness of cloud: 10
- homogeneous extinction coefficient in cube
- optical properties as for case C 1 (step cloud)
- single scattering albedo: 1.0
- effective radius: 10 $\mu$m
- Lambertian surface albedo: 0.2
- Solar azimuth angle $\phi_0$=0$^\circ$
- Viewing geometries (solar zenith angle $\theta_0$, output altitude $z$, viewing zenith angle $\theta$ and viewing azimuth angle $\phi$):
| # | $\theta_0$ [$^\circ$] | $z$ [km] | $\theta$ [$^\circ$] | $\phi$ [$^\circ$] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 0 | 40 | 0 |
| 2 | 20 | 0 | 40 | 60 |
| 3 | 20 | 0 | 40 | 120 |
| 4 | 20 | 0 | 40 | 180 |
| 5 | 40 | 5 | 180 | 0 |
| 6 | 40 | 5 | 140 | 0 |
| 7 | 40 | 5 | 140 | 60 |
| 8 | 40 | 5 | 140 | 120 |
| 9 | 40 | 5 | 140 | 180 |
- first set of simulations: cubic cloud in vacuum
- second set of simulations: cubic cloud in homogeneous Rayleigh scattering layer with optical thickness of 0.5, depolarization factor 0
Note on azimuth convention:
270
+++++++++++++++++high Y
| |
| |
| |
0 deg | | 180
| |
| |
++++++++++++++++++low Y
90
low X high X
Output format:
The output should be provided in an ascii file containing the following columns:
case theta_0 z theta phi i_x i_y I Q U V Istd Qstd Ustd Vstd
case should be set to 1 for the simulations in vacuum and 2 for the case with Rayleigh scattering.
i_x and i_y denotes the pixel numbers in x and y direction respectively (starting with 1).
I,Q,U,V denote the Stokes vector.
Istd Qstd Ustd Vstd are standard deviations of the Stokes vector components which should be provided for Monte Carlo models. If error estimates can not be provided, these columns may be omitted.
The result filename should be 'iprt_case_C2_MODEL.dat' and it should include the following header:
# IPRT case C2 - Cubic cloud # RT model: MODEL_NAME # case theta_0 z theta phi i_x i_y I Q U V Istd Qstd Ustd Vstd
Results
Example result:
General
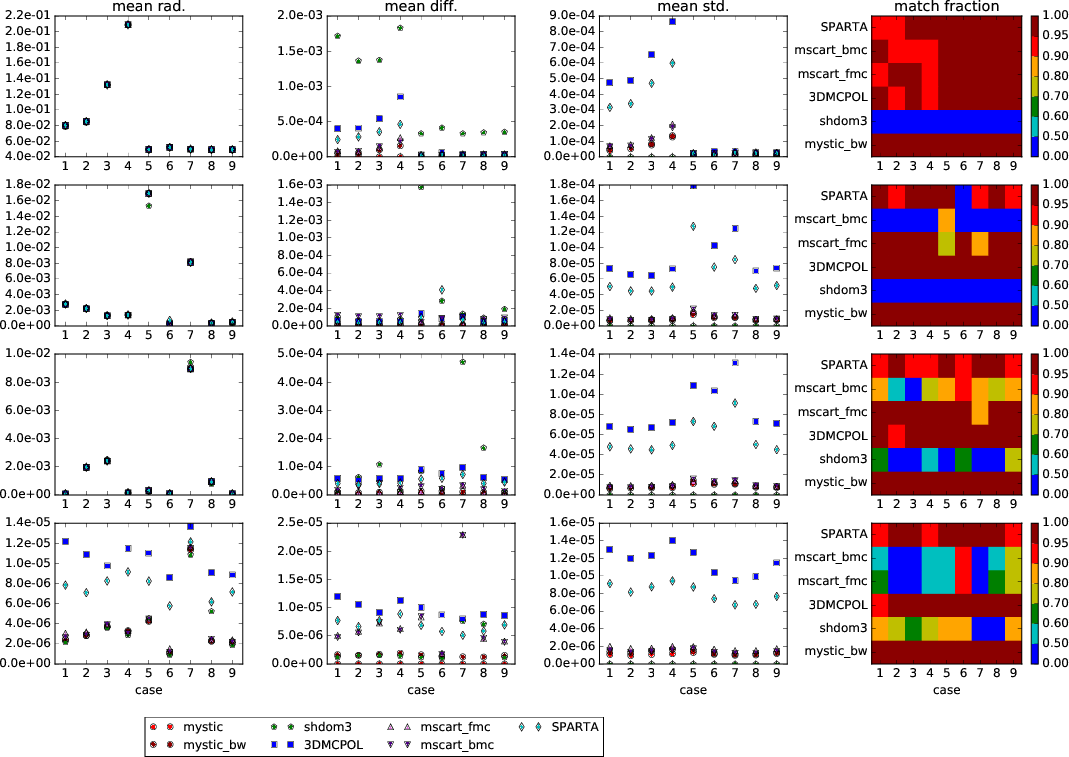
- Generally we find a very good agreement between all Monte Carlo models, only for a few cases they do not agree within 2 standard deviations.
- For SHDOM a quantitative comparison is difficult because it does not provide a standard deviation and systematic differences are expected (different treatment of cloud boundary. Smaller differences due to different solution method of VRTE).
- MSCART (backward mode) shows sytematic differences to the forward calculations, Wang Zhen already mentioned this. MYSTIC gives the same results in forward and backward mode.
- The agreed number of photons for this case is 49e9, this number has been used for 3DMCPOL, MSCART and MYSTIC. For SPARTA, 10e11 photons were used
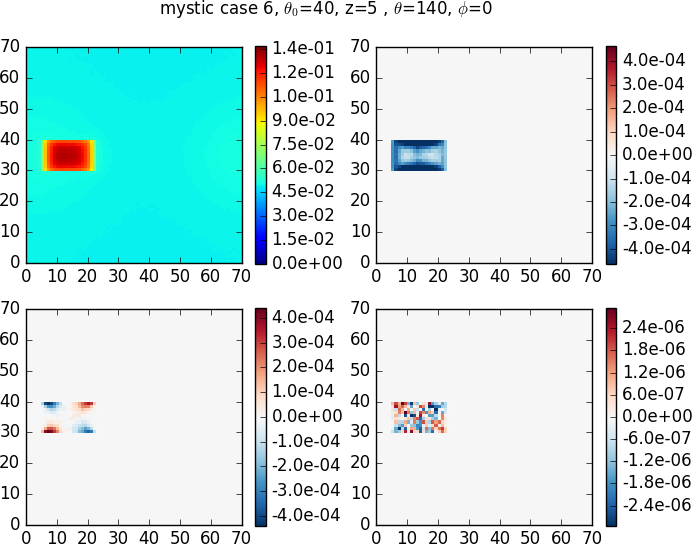
The following plots show the mean radiance (for each Stokes component), mean absolute difference with respect to MYSTIC (forward Monte Carlo), mean standard deviation, fraction of pixels which agree within 2 standard deviations. Only pixels with non-zero radiances are included into the statistics.
 Summary plots, statistics C2 without atmosphere
Summary plots, statistics C2 without atmosphere
work in progress …
- Stokes component I (upper row): The mean radiance (average over all non-zero pixels) is very similar for all models. The mean absolute difference is smaller than 1\% of the mean radiance. The mean differences are largest for SHDOM. Models without variance reduction (3DMCPOL, SPARTA) show larger differences than models with variance reduction (MSCART, MYSTIC-backward). Also the standard deviations are much smaller when variance reduction techniques are used (as expected).
The match fraction shows that all Monte Carlo models agree within 2 <m>sigma<\m> for cases 5-9 (down-looking). The match fraction is between 0.9 and 0.95 for some up-looking cases 1-4, which indicates a small bias between other models and MYSTIC. MYSTIC (forward and backward mode) agree perfectly. - Stokes component Q (second row): The first column shows the mean absolute radiance (since Q can be positive or negative). The only visible difference in mean radiance is seen for case 5, here SHDOM is smaller than the Monte Carlo models, the difference is about 10%.
Mean standard deviations again are larger for models without variance reduction. The match fraction shows obvious sytematic differences for mscart_bmc (all cases), mscart_fmc (cases 5 and 7) and SPARTA (case 6). - Stokes component U (third row): Largest difference for case 7, mean difference between SHDOM and MYSTIC is about 5% of mean radiance. The match fraction shows obvious sytematic differences for mscart_bmc (all cases), mscart_fmc (case 7).
- Stokes component V (bottom): Very noisy, without variance reduction radiance has same order of magnitude as standard deviation. The match fraction shows sytematic differences for mscart_bmc and mscart_fmc (all cases).
Results without atmosphere
Statistics plots
Stokes parameters I,Q,U,V
Differences to MYSTIC
Results with atmosphere
Statistics plots
Stokes parameters I,Q,U,V
The range of the colorbars corresponds to the minimum and the maximum of the SHDOM results. For V all Monte Carlo models show quite strong noise, therefore the best is to choose the explicit model to set the limits.
Differences to MYSTIC
Here the colorbar limits correspond to 5% of the minimum and maximum of the MYSTIC results.