Sidebar
teaching:radiative_transfer:halo
Table of Contents
Ice clouds - halo and crystal shape
Investigate the radiance field in presence of an ice cloud. What do you observe? What is the impact of the crystal shape?
An ice cloud can be defined in the libRadtran input file as follows:
- ic.inp
ic_properties hey interpolate ic_habit solid-column
Please refer to the libRadtran user manual to find out which crystal shapes are available. In order to use the HEY parameterization you have to copy the following data:
cp -r /home/data/daten/public/rt-data/optprop_data/ic/ /local/libRadtran-1.5-beta/data/
Use the libRadtran input file and the plotting script from exercise 6 to start.
Solution by Sebastian and Hanna
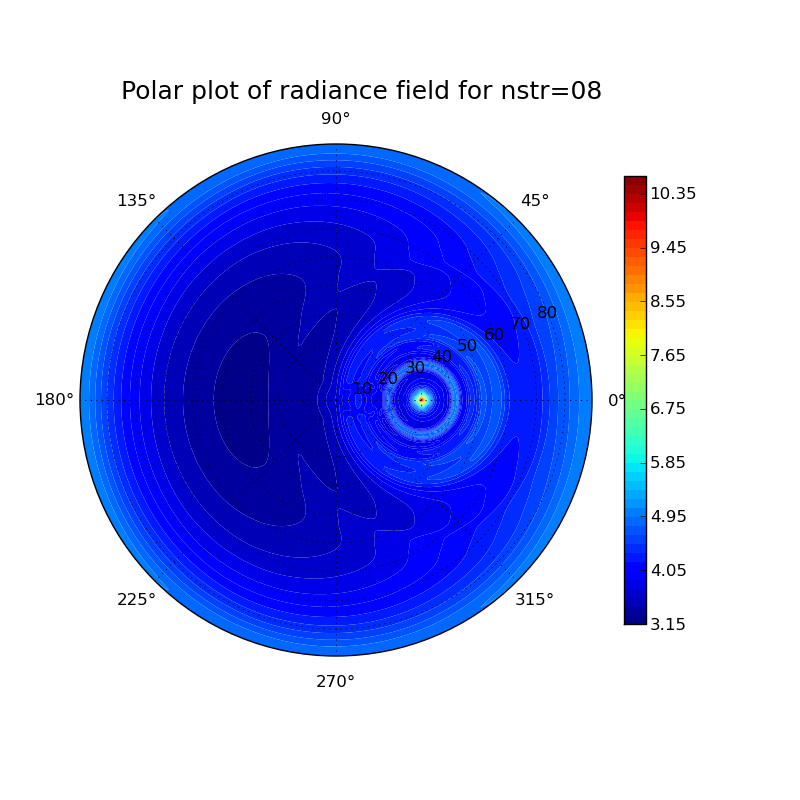
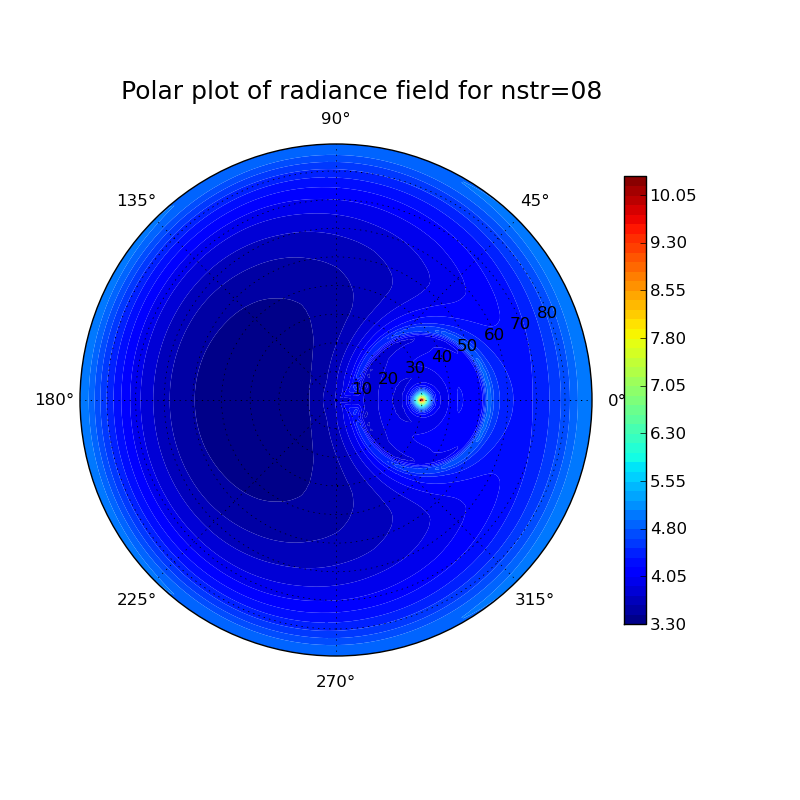
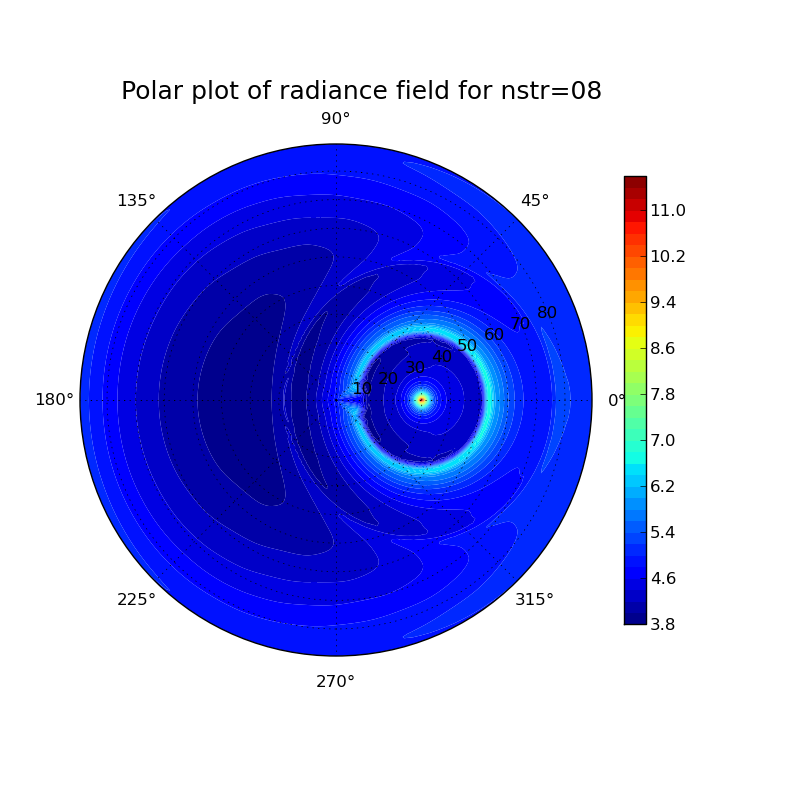
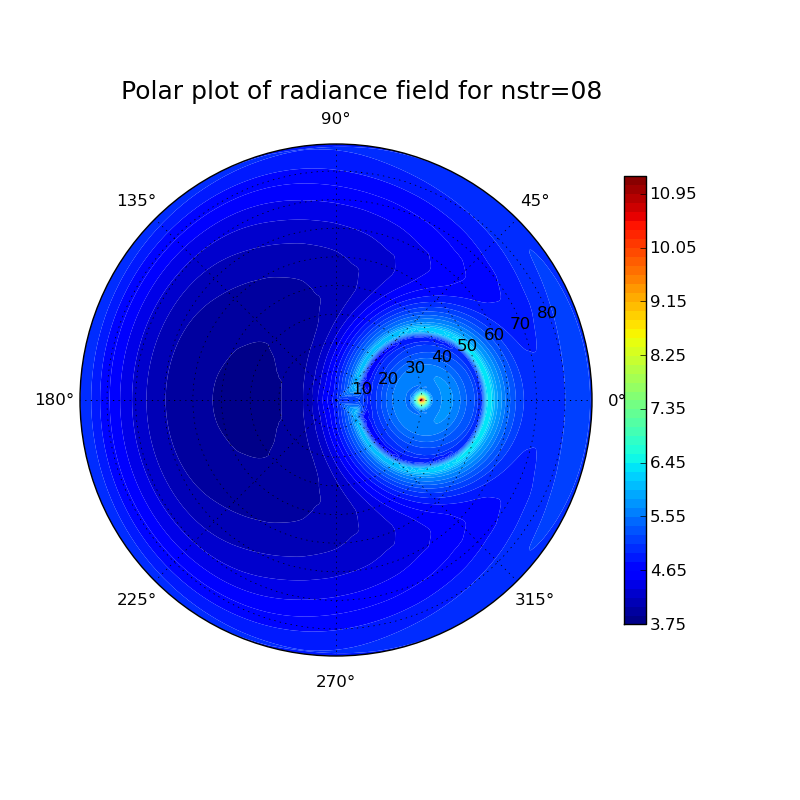
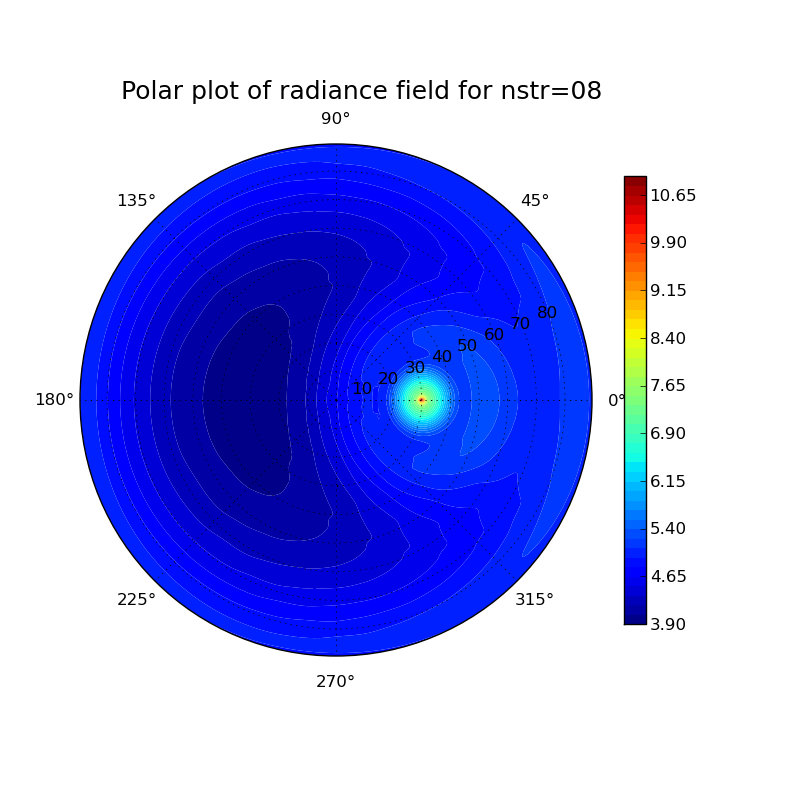
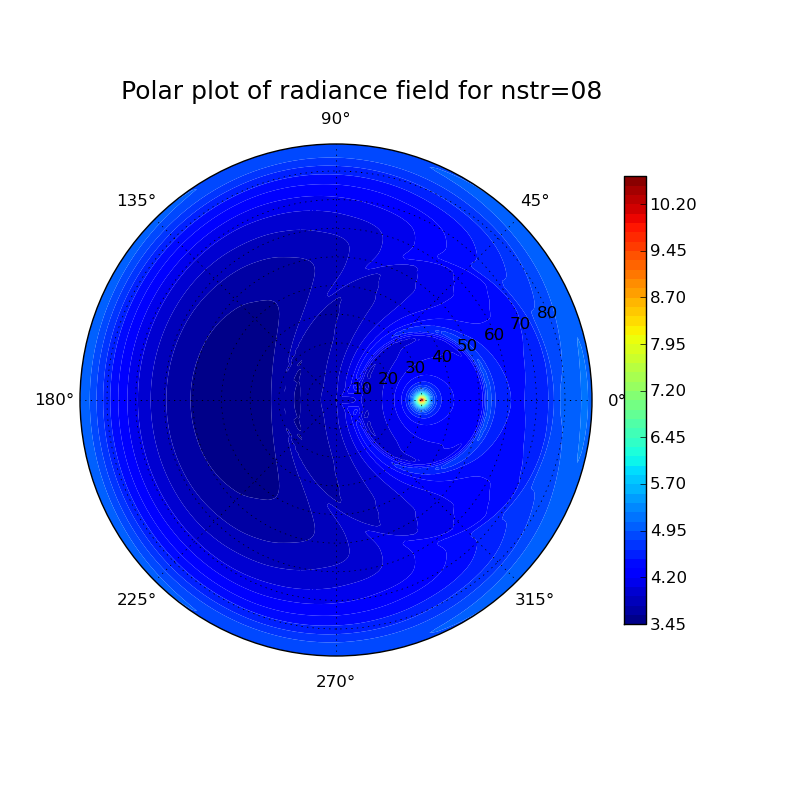
Investigation of different particle shapes and cloud thicknesses
Cloud properties: [(height) (ice water content) (particle size)]
thin cloud
11 0 0 10 0.001 30
thick cloud
11 0 0 10 0.006 70 09 0.01 90 08 0.004 50 07 0 0
Plots for different particle shapes at a solar zenith angle of 30° and a wavelength of 500 nm:
thin cloud:
thick cloud:
teaching/radiative_transfer/halo.txt · Last modified: 2018/05/04 08:40 (external edit)
Except where otherwise noted, content on this wiki is licensed under the following license: GNU Free Documentation License 1.3